Heat of Sublimation Can Be Approximated by Adding Together
ane
one) Crystalline solids ________.
A) have their particles arranged randomly
B) have highly ordered structures
C) are normally very soft
D) be simply at high temperatures
E) be only at very low temperatures
B) accept highly ordered structures
two
two) In liquids, the attractive intermolecular forces are ________.
A) very weak compared with kinetic energies of the molecules
B) strong enough to hold molecules relatively shut together
C) potent enough to go along the molecules bars to vibrating about their fixed lattice points
D) not strong enough to go on molecules from moving past each other
Eastward) strong enough to hold molecules relatively shut together only not strong enough to go on molecules from moving past each other
East) stiff enough to hold molecules relatively close together just not strong enough to keep molecules from moving past each other
3
iii) Every bit a gaseous chemical element condenses, the atoms get ________ and they have ________ attraction for one some other.
A) more separated, more than
B) more separated, less
C) closer together, more than
D) closer together, less
East) larger, greater
iv
4) A gas is ________ and assumes ________ of its container, whereas a liquid is ________ and assumes ________ of its container.
A) compressible, the volume and shape, not compressible, the shape of a portion
B) compressible, the shape, not compressible, the volume and shape
C) compressible, the volume and shape, compressible, the volume
D) condensed, the volume and shape, condensed, the book and shape
Due east) condensed, the shape, compressible, the volume and shape
A) compressible, the book and shape, not compressible, the shape of a portion
v
5) Together, liquids and solids constitute ________ phases of matter.
A) the compressible
B) the fluid
C) the condensed
D) all of the
E) the disordered
six
half dozen) Which statement is truthful well-nigh liquids but not true nearly solids?
A) They flow and are highly ordered.
B) They are highly ordered and not compressible.
C) They catamenia and are compressible.
D) They presume both the book and the shape of their containers.
Eastward) They flow and are non compressible.
C) They menses and are compressible.
7
seven) The strongest interparticle attractions exist between particles of a ________, and the weakest interparticle attractions exist betwixt particles of a ________.
A) solid, liquid
B) solid, gas
C) liquid, gas
D) liquid, solid
Eastward) gas, solid
eight
viii) Of the following substances, simply ________ has London dispersion forces as the but intermolecular force.
A) CH3OH
B) NHiii
C) H2Due south
D) Kr
E) HCl
9
ix) In which of the following molecules is hydrogen bonding likely to exist the most significant component of the total intermolecular forces?
A) CHfour
B) CfiveH11OH
C) C6H13NH2
D) CHiiiOH
E) CO2
ten
x) Which of the following has dispersion forces every bit its only intermolecular force?
A) CH4
B) HCl
C) C6H13NH2
D) NaCl
Due east) CH3Cl
xi
11) When NaCl dissolves in water, aqueous Na+ and Cl- ions issue. The forcefulness of allure that exists between Na+ and H2O is chosen a(northward) ________ interaction.
A) dipole-dipole
B) ion-ion
C) hydrogen bonding
D) ion-dipole
Due east) London dispersion force
12
12) ________ are particularly polarizable.
A) Small nonpolar molecules
B) Small polar molecules
C) Large nonpolar molecules
D) Large polar molecules
E) Large molecules, regardless of their polarity,
Eastward) Large molecules, regardless of their polarity,
13
13) The ease with which the charge distribution in a molecule can be distorted by an external electrical field is chosen the ________.
A) electronegativity
B) hydrogen bonding
C) polarizability
D) volatility
E) viscosity
14
14) The intermolecular force(due south) responsible for the fact that CH4 has the lowest boiling point in the set up CH4, SiH4, GeH4, SnH4 is/are ________.
A) hydrogen bonding
B) dipole-dipole interactions
C) London dispersion forces
D) mainly hydrogen bonding but also dipole-dipole interactions
Due east) mainly London-dispersion forces simply likewise dipole-dipole interactions
C) London dispersion forces
xv
15) Elemental iodine (I2) is a solid at room temperature. What is the major bonny forcefulness that exists among different I2 molecules in the solid?
A) London dispersion forces
B) dipole-dipole rejections
C) ionic-dipole interactions
D) covalent-ionic interactions
E) dipole-dipole attractions
A) London dispersion forces
16
16) Hydrogen bonding is a special example of ________.
A) London-dispersion forces
B) ion-dipole allure
C) dipole-dipole attractions
D) ion-ion interactions
E) none of the above
C) dipole-dipole attractions
17
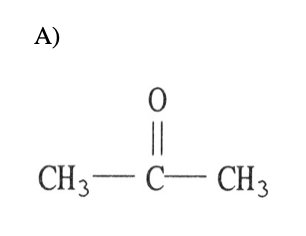
17) Which one of the following substances will have hydrogen bonding as i of its intermolecular forces?
eighteen
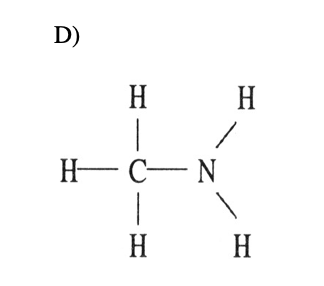
18) Which one of the post-obit substances will non have hydrogen bonding as ane of its intermolecular forces?
19
19) What intermolecular force is responsible for the fact that water ice is less dense than liquid water?
A) London dispersion forces
B) dipole-dipole forces
C) ion-dipole forces
D) hydrogen bonding
Due east) ionic bonding
20
20) The predominant intermolecular strength in (CH3)2NH is ________.
A) London dispersion forces
B) ion-dipole forces
C) ionic bonding
D) dipole-dipole forces
East) hydrogen bonding
21
21) C12H26 molecules are held together by ________.
A) ion-ion interactions
B) hydrogen bonding
C) ion-dipole interactions
D) dipole-dipole interactions
E) dispersion forces
22
22) Which of the following molecules has hydrogen bonding equally its merely intermolecular strength?
A) HF
B) H2O
C) C6H13NH2
D) C5H11OH
E) None, all of the in a higher place showroom dispersion forces.
East) None, all of the above exhibit dispersion forces.
23
23) Which of the following molecules has hydrogen bonding every bit its only intermolecular force?
A) NH3
B) H2O
C) C3H7OH
D) HOCH2CH2OH
Eastward) None, all of the in a higher place exhibit dispersion forces.
East) None, all of the above showroom dispersion forces.
24
24) What types of intermolecular forces exist between Howdy and H2South?
A) dipole-dipole and ion-dipole
B) dispersion forces, dipole-dipole, and ion-dipole
C) dispersion forces, hydrogen bonding, dipole-dipole, and ion-dipole
D) dispersion forces and dipole-dipole
Eastward) dispersion forces and ion-dipole
D) dispersion forces and dipole-dipole
25
5) What type(s) of intermolecular forces exist betwixt Br2 and CCl4?
A) dispersion forces
B) dispersion forces and ion-dipole
C) dispersion forces and dipole-dipole
D) dispersion forces, ion-dipole, and dipole-dipole
Eastward) None. Since both are gases at room temperature, they do not interact with each other.
26
26) What type(s) of intermolecular forces exist between PH3 and COthree 2 -?
A) dispersion forces
B) dispersion forces and ion-dipole
C) dispersion forces, ion-dipole, and dipole-dipole
D) dispersion forces and dipole-dipole
East) dispersion forces, ion-dipole, dipole-dipole, and hydrogen bonds
B) dispersion forces and ion-dipole
27
27) What types of intermolecular forces exist between NH3 and H2S?
A) dispersion forces and dipole-dipole forces
B) dispersion forces
C) dispersion forces and hydrogen bonds
D) dispersion forces, hydrogen bonds, and dipole-dipole forces
E) dispersion forces, hydrogen bonds, and ion-dipole forces
A) dispersion forces and dipole-dipole forces
28
28) What types of intermolecular forces exist between NH3 and HF?
A) dispersion forces and dipole-dipole forces
B) dispersion forces and hydrogen bonds
C) dispersion forces, dipole-dipole forces, and hydrogen bonds
D) dispersion forces
Due east) dispersion forces, hydrogen bonds, and ion-dipole forces
C) dispersion forces, dipole-dipole forces, and hydrogen bonds
29
29) ________ is the energy required to expand the surface area of a liquid past a unit amount of surface area.
A) Viscosity
B) Surface tension
C) Volatility
D) Meniscus
Eastward) Capillary action
xxx
thirty) Which statements about viscosity are true?
(i) Viscosity increases every bit temperature decreases.
(ii) Viscosity increases as molecular weight increases.
(iii) Viscosity increases as intermolecular forces increase.
A) (i) only
B) (ii) and (iii)
C) (i) and (iii)
D) none
E) all
31
31) The shape of a liquid's meniscus is determined by ________.
A) the viscosity of the liquid
B) the type of fabric the container is fabricated of
C) the relative magnitudes of cohesive forces in the liquid and adhesive forces between the liquid and its container
D) the amount of hydrogen bonding in the liquid
E) the volume of the liquid
C) the relative magnitudes of cohesive forces in the liquid and adhesive forces betwixt the liquid and its container
32
32) Viscosity is ________.
A) the "pare" on a liquid surface acquired by intermolecular allure
B) the resistance to menstruation
C) the same every bit density
D) inversely proportional to molar mass
E) unaffected by temperature
B) the resistance to catamenia
33
33) How high a liquid will rise up a narrow tube as a result of capillary action depends on ________.
A) the magnitudes of cohesive forces in the liquid and adhesive forces betwixt the liquid and the tube, and gravity
B) gravity solitary
C) only the magnitude of adhesive forces between the liquid and the tube
D) the viscosity of the liquid
E) only the magnitude of cohesive forces in the liquid
A) the magnitudes of cohesive forces in the liquid and adhesive forces between the liquid and the tube, and gravity
34
34) The property responsible for the "beading upwardly" of water is ________.
A) density
B) viscosity
C) vapor force per unit area
D) surface tension
E) hydrogen bonding
35
35) Rut of sublimation tin can be approximated past calculation together ________ and ________.
A) heat of fusion, heat of condensation
B) estrus of fusion, heat of vaporization
C) oestrus of freezing (solidification), heat of condensation
D) heat of freezing (solidification), estrus of vaporization
Eastward) heat of deposition, heat of vaporization
B) heat of fusion, heat of vaporization
36
36) Which of the following statements is imitation?
A) The accented value of the heat of sublimation is equal to the accented value of the heat of deposition.
B) The heat of sublimation is equal to the sum of the estrus of vaporization and the heat of melting.
C) The heat of sublimation is equal to the sum of the rut of vaporization and the oestrus of freezing.
D) The absolute value of the oestrus of sublimation is equal to the accented value of the sum of the rut of condensation and the rut of freezing.
E) The absolute value of the heat of deposition is equal to sum of the absolute value of the oestrus of vaporization and the absolute value of the oestrus of freezing.
C) The heat of sublimation is equal to the sum of the heat of vaporization and the oestrus of freezing.
37
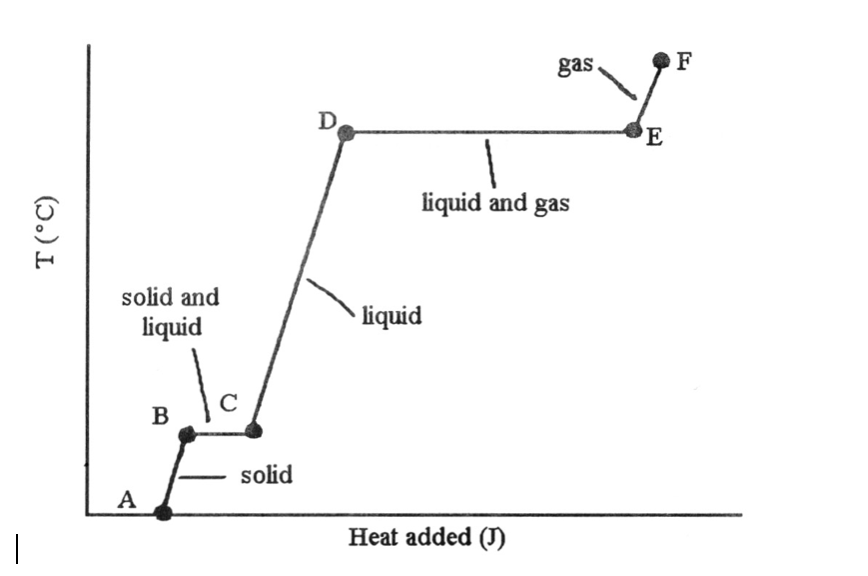
37) The stage changes B → C and D → Eastward are not associated with temperature increases because the heat energy is used upward to ________.
A) increase distances betwixt molecules
B) suspension intramolecular bonds
C) rearrange atoms within molecules
D) increment the velocity of molecules
E) increase the density of the sample
A) increase distances between molecules
38
38) Based on the following information, which compound has the strongest intermolecular forces?
Substance ΔH vap (kJ/mol)
Argon (Ar) 6.3
Benzene (C6H6)31.0
Ethanol (C2H5OH)39.3
H2o (H2o)40.8
Methane (CH4)9.2
A) Argon
B) Benzene
C) Ethanol
D) Water
E) Methyl hydride
39
39) Which compound has the strongest intermolecular forces?
A) CBr4
B) C12H26
C) CI4
D) Due north2
Due east) O2
40
twoscore) Large intermolecular forces in a substance are manifested past ________.
A) low vapor pressure
B) high boiling betoken
C) high heats of fusion and vaporization
D) loftier critical temperatures and pressures
E) all of the in a higher place
41
41) A substance that expands to fill its container however has a density budgeted that of a liquid, and that can acquit as a solvent is called a(n) ________.
A) plasma
B) gas
C) liquid
D) amorphous solid
E) supercritical fluid and gas
Due east) supercritical fluid and gas
42
42) The critical temperature and pressure of CS2 are 279 °C and 78 atm, respectively. At temperatures in a higher place 279 °C and pressures above 78 atm, CS2 can simply occur as a ________.
A) solid
B) liquid
C) liquid and gas
D) gas
East) supercritical fluid
43
43) The substance with the largest heat of vaporization is ________.
A) I2
B) Brii
C) Cl2
D) F2
East) O2
44
44) Of the following, ________ is an exothermic process.
A) melting
B) subliming
C) freezing
D) humid
Eastward) All of the above are exothermic.
45
45) Of the following, ________ should have the highest critical temperature.
A) CBr4
B) CCl4
C) CF4
D) CH4
East) Hii
46
46) A volatile liquid is one that ________.
A) is highly flammable
B) is highly viscous
C) is highly hydrogen-bonded
D) is highly cohesive
E) readily evaporates
47
47) In general, the vapor pressure of a substance increases as ________ increases.
A) surface tension
B) molecular weight
C) hydrogen bonding
D) viscosity
E) temperature
48
48) The vapor pressure of any substance at its normal boiling point is
A) i Pa
B) i torr
C) 1 atm
D) equal to atmospheric pressure
Eastward) equal to the vapor pressure level of water
49
49) Volatility and vapor pressure are ________.
A) inversely proportional to 1 another
B) directly proportional to one another
C) not related
D) the same thing
E) both contained of temperature
B) direct proportional to one some other
50
50) Some things have longer to cook at high altitudes than at low altitudes because ________.
A) water boils at a lower temperature at high altitude than at depression distance
B) water boils at a higher temperature at high distance than at low altitude
C) oestrus isn't conducted as well in low density air
D) natural gas flames don't burn as hot at high altitudes
E) there is a higher moisture content in the air at high altitude
A) h2o boils at a lower temperature at high distance than at low distance
51
51) The vapor force per unit area of a liquid ________.
A) increases linearly with increasing temperature
B) increases nonlinearly with increasing temperature
C) decreases linearly with increasing temperature
D) decreases nonlinearly with increasing temperature
Due east) is totally unrelated to its molecular structure
B) increases nonlinearly with increasing temperature
52
53) On a phase diagram, the critical force per unit area is ________.
A) the pressure required to melt a solid
B) the pressure level below which a substance is a solid at all temperatures
C) the force per unit area in a higher place which a substance is a liquid at all temperatures
D) the force per unit area at which a liquid changes to a gas
East) the force per unit area required to liquefy a gas at its critical temperature
East) the pressure required to liquefy a gas at its critical temperature
53
54) On a stage diagram, the critical temperature is ________.
A) the temperature below which a gas cannot be liquefied
B) the temperature above which a gas cannot be liquefied
C) the temperature at which all iii states are in equilibrium
D) the temperature required to melt a solid
E) the temperature required to cause sublimation of a solid
B) the temperature above which a gas cannot be liquefied
54
55) On a phase diagram, the melting point is the aforementioned every bit ________.
A) the triple point
B) the critical signal
C) the freezing point
D) the boiling point
E) the vapor-force per unit area curve
55
56) When the phase diagram for a substance has a solid-liquid phase purlieus line that has a negative slope (leans to the left), the substance ________.
A) tin go from solid to liquid, within a modest temperature range, via the awarding of pressure level
B) sublimes rather than melts under ordinary weather
C) cannot become from solid to liquid by application of pressure at any temperature
D) cannot be liquefied in a higher place its triple point
E) melts rather than sublimes under ordinary conditions
A) can become from solid to liquid, within a small temperature range, via the application of pressure
56
57) The predominant intermolecular forcefulness in CaBr2 is ________.
A) London-dispersion forces
B) ion-dipole forces
C) ionic bonding
D) dipole-dipole forces
Due east) hydrogen bonding
57
58) Which of the following is most likely to showroom liquid-crystalline behavior?
A) CH3CH2-C(CH3)2-CH2CH3
B) CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3
C) CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2-
D)
E)
58
59) Which of the post-obit characteristics would prevent liquid crystal beliefs?
A) long axial structure
B) ionic configuration
C) carbon-carbon single bonds
D) double bonding
E) polar groups
59
sixty) In the smectic A liquid-crystalline phase, ________.
A) the molecules are aligned along their long axes, with no ordering with respect to the ends of the molecules
B) the molecules are arranged in sheets, with their long axes parallel and their ends aligned likewise
C) the molecules are aligned with their long axes tilted with respect to a line perpendicular to the plane in which the molecules are stacked
D) deejay-shaped molecules are aligned through a stacking of the disks in layers
E) the molecules are oriented in a totally random style
B) the molecules are arranged in sheets, with their long axes parallel and their ends aligned besides
pendletonmandeseent.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.easynotecards.com/notecard_set/104834
0 Response to "Heat of Sublimation Can Be Approximated by Adding Together"
Post a Comment